Amphetamine Addiction Treatment
Amphetamine Addiction Treatment and Detox Program
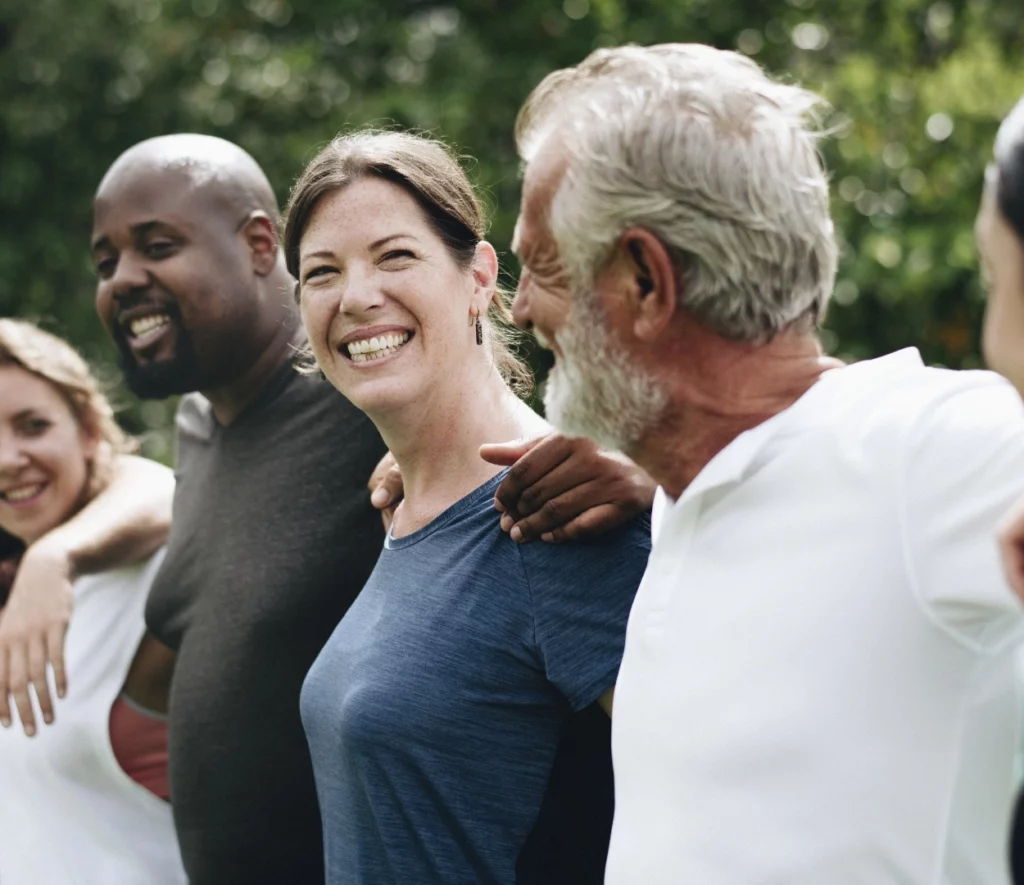
Amphetamine addiction is a pervasive and growing public health issue in the United States, with a profound impact on both individuals and society. Amphetamines, including drugs like methamphetamine, are central nervous system stimulants that are commonly abused due to their euphoric effects, which include increased energy, heightened focus, and a sense of well-being. However, continued use of these substances leads to serious physical and psychological dependence, resulting in detrimental consequences for users. According to the Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA, 2022), approximately 1.8 million people in the U.S. reported having a substance use disorder related to amphetamines and other prescription stimulants. This alarming statistic highlights the urgent need for comprehensive amphetamine addiction treatment strategies and detoxification programs designed to address the specific challenges of amphetamine addiction.
Individuals may experience intense cravings and psychological distress throughout the recovery process. However, with evidence-based treatment methods, including behavioral therapies and medically assisted detox at a trusted addiction treatment center, Legacy Healing Center can help individuals break free from the grip of addiction and reclaim their lives. Our addiction specialists explore the process of amphetamine detox, effective treatment options, and the importance of professional care in achieving long-term recovery.
Ladies and Gentlemen,
Caring for Ladies
and Gentlemen.
888-534-2295What Are Amphetamines?
Amphetamines are a class of powerful central nervous system stimulants used medically to treat certain conditions such as attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), narcolepsy, and obesity. While prescription medications like Adderall and Dexedrine can improve focus and reduce impulsivity, the drug’s euphoric effects also contribute to its high abuse potential.
What Makes Amphetamines Addictive?
The addictive potential of amphetamines lies in their ability to elevate the levels of certain neurotransmitters, including dopamine, norepinephrine, and serotonin. These chemicals are responsible for regulating mood, alertness, and pleasure. By artificially increasing these levels, amphetamines induce intense feelings of euphoria, increased energy, and enhanced focus. This rush of pleasurable effects is what often drives individuals to abuse the drug.
However, repeated use of amphetamines leads to neuroadaptation, meaning the brain becomes reliant on the drug to function normally. Over time, the brain’s natural production of dopamine decreases, and the individual develops a tolerance to the drug, needing larger amounts to achieve the same effects. As a result, individuals may continue to use amphetamines, even in the face of negative consequences, to stave off withdrawal symptoms or to experience the desired high.
This cycle of dependence and tolerance places significant stress on both the brain and body, creating a complex and powerful addiction that requires medical intervention to break.
Signs of Amphetamine Addiction
Amphetamine addiction is a complex condition that affects both the body and mind. While the immediate effects may seem desirable, prolonged use can lead to severe physical, psychological, and social consequences. Understanding the signs of amphetamine addiction as well as the impact on physical and mental health is crucial in order to identify the need for treatment and support.
Behavioral Signs of Amphetamine Addiction
Addiction to amphetamines often manifests through changes in behavior that are driven by the compulsive need to use the drug. These behaviors can lead to a breakdown in personal relationships and neglect of important responsibilities.
- Compulsive drug-seeking behavior: Individuals may go to great lengths to obtain amphetamines, even if it involves illegal activities or unethical behavior. This could include stealing, engaging in risky transactions, or exploiting others. Intrusive thoughts about using the drug or acquiring more can dominate the individual’s mind, leading to obsessive behavior.
- Increased frequency of use: The person may begin using amphetamines more often, using them at inappropriate times or in larger quantities.
- Neglecting personal hygiene and responsibilities: As addiction intensifies, individuals may lose interest in personal care or fulfilling work, school, or family obligations.
- Social withdrawal: Individuals with amphetamine addiction may begin isolating themselves from friends and family, spending more time alone or with others who enable their drug use.
- Engaging in risky behaviors: Amphetamine use can impair judgment and lead to risky decisions, such as driving while under the influence, engaging in unsafe sexual practices, or using the drug in dangerous environments.
Physical Signs of Amphetamine Abuse
The physical effects of amphetamine use are striking and can cause significant damage over time. When someone first uses amphetamines, the immediate effects are part of the appeal, especially for those who are seeking enhanced focus, energy, or mood elevation. However, these short-term effects can also signal the beginning of potential dependency and addiction. Common short-term effects of amphetamine use include:
Short-Term Effects of Amphetamine Use
- Euphoria: A rush of pleasure or excitement, often accompanied by a sense of increased confidence
- Increased energy and alertness
- Elevated heart rate and blood pressure
- Decreased appetite
- Dilated pupils
- Sleep disturbances: Due to the stimulating effects, users may struggle to fall asleep or stay asleep for extended periods.
Long-Term Effects of Amphetamine Use
When amphetamines are used over extended periods, the long-term effects can be profoundly damaging. The body and brain undergo significant changes, and the negative consequences can affect nearly every aspect of a person’s health, from their physical well-being to their cognitive function and mental health.
- Cardiovascular problems: Long-term use increases the risk of serious heart problems, including arrhythmias (irregular heartbeats), heart attack, and stroke, due to the heightened strain on the heart and blood vessels.
- Weight loss and malnutrition: Due to its appetite-suppressing effects, users may experience significant and unhealthy weight loss, which can lead to malnutrition and associated health problems.
- Severe dental decay (“Meth mouth”): A particularly notable issue in long-term users, amphetamines contribute to severe dental decay due to dry mouth, poor hygiene, and dietary neglect.
- Skin sores and infections: People who inject amphetamines may develop skin sores or abscesses, which can become infected if left untreated.
- Cognitive decline: Long-term amphetamine use can affect cognitive functions, such as memory, attention, and learning. These effects can be permanent or take significant time to recover from after ceasing use.
Impact on Daily Life and Mental Health
Amphetamine addiction profoundly affects an individual’s daily life and overall mental health. As tolerance builds, the negative consequences become more apparent. The social and behavioral effects, such as isolation, financial problems, and damaged relationships, often exacerbate mental health challenges, creating a vicious cycle that further entrenches addiction.
- Isolation: As the addiction progresses, individuals may start to withdraw from family, friends, and social networks. They may avoid social gatherings or avoid people who disapprove of their drug use, further exacerbating their isolation.
- Relationships: Amphetamine addiction can strain relationships with family members, friends, and romantic partners. Loved ones may feel hurt, betrayed, or neglected, leading to conflict or separation. The person may withdraw emotionally, act irritably, or become defensive when confronted about their behavior. This can create a cycle of loneliness and emotional pain, which may drive the person back to using amphetamines as a form of coping.
- Difficulty maintaining work or education: As a result of the cognitive and behavioral effects of amphetamine addiction, maintaining a job or academic performance becomes increasingly difficult. Frequent absences, poor decision-making, and a lack of focus may result in job loss or academic failure, further contributing to a cycle of stress and emotional distress.
- Legal and financial troubles: The compulsion to use amphetamines often leads individuals into illegal activities (such as drug possession, distribution, or theft), which can result in criminal charges, arrests, or significant legal consequences. Additionally, the financial cost of maintaining a drug habit can lead to financial instability, debts, and even bankruptcy.
Mental Health Effects of Amphetamine Use
The long-term effects of amphetamine use and addiction are particularly detrimental to an individual’s mental health. The intense highs and crashes associated with the drug disrupt the brain’s natural ability to regulate mood and emotions. These psychological consequences can make it even harder to break the cycle of addiction, as the person may rely on the drug to alleviate the emotional turmoil it causes.
- Anxiety and paranoia: Chronic use of amphetamines can trigger persistent feelings of anxiety, nervousness, and, in some cases, paranoia.
- Aggression: People using amphetamines may experience mood swings and aggressive behavior, sometimes lashing out without provocation.
- Depression: As the brain’s natural balance of neurotransmitters is disrupted, many users report feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and low energy during periods of withdrawal or after prolonged use.
- Psychosis: In extreme cases, chronic use can lead to amphetamine-induced psychosis, which may include hallucinations, delusions, and loss of reality. These symptoms can persist long after the drug is no longer in the system, often requiring professional psychiatric intervention.ptcy.
Amphetamine addiction is a serious condition that not only affects physical health but also disrupts relationships, career prospects, and mental stability. Recognizing the signs of amphetamine addiction and understanding its effects are key to seeking the appropriate help and treatment. The road to recovery may be long, but with the support offered at Legacy Healing Center, individuals can reclaim control over their lives and begin the healing process.
Why Amphetamine Detox Is Crucial for Recovery
Amphetamine detoxification is the first and most critical step in the recovery process; it helps individuals safely manage withdrawal symptoms and begin to break the cycle of dependency.
- A medically managed detox process allows medical professionals to monitor withdrawal symptoms, administer medications, and implement interventions, which reduces the risk of serious health complications.
- This step also provides individuals with the support they need to address not just the physical dependence on amphetamines but also the emotional and psychological aspects of addiction.
Without proper detox, individuals may face significant hurdles in their recovery journey. Ultimately, medically supervised detox is essential to ensure a safe, effective, and sustainable recovery from amphetamine addiction.
The Dangers of a Detox at Home
Detoxing from amphetamines without professional supervision is dangerous. Withdrawal can cause severe symptoms, and in extreme cases, life-threatening conditions such as heart arrhythmias and seizures. Self-detoxing increases the risk of relapse, as individuals often use the drug again to alleviate unbearable symptoms, creating a harmful cycle. This is why seeking professional help is essential to ensure a safe and effective recovery.
Amphetamine Detox Timeline
Amphetamine detox typically unfolds in three distinct stages, each with its own set of challenges and timeframes. The stages help medical professionals assess and manage the individual’s symptoms while providing necessary interventions.
- Initial Phase (First 6-12 hours): The initial phase occurs shortly after an individual stops using amphetamines. During this time, withdrawal symptoms begin to appear, often accompanied by profound emotional and physical discomfort.
- Peak Phase (48-72 hours): The peak phase is typically the most intense phase of amphetamine detox. The individual may feel a strong urge to use again in order to alleviate these uncomfortable feelings; medical support is essential to help the person cope with the overwhelming physical and emotional symptoms.
- Resolution Phase (Up to a week): After the worst of the withdrawal symptoms begin to subside, the individual enters the resolution phase. While the immediate symptoms may lessen, individuals may still experience lingering cravings, mood instability, and fatigue, so emotional and psychological support is crucial.
The detox process is an essential first step in overcoming amphetamine addiction, as it helps to break the physical dependence on the drug. Professional support during detox ensures that individuals can transition to the next stage of recovery with the tools and strategies necessary to avoid relapse and maintain long-term sobriety. Detox is just the beginning, but with the right care, it paves the way for a successful recovery journey.
Amphetamine Addiction Treatment Options
When it comes to treating amphetamine addiction, choosing the right program is essential. Treatment programs generally fall into two main categories: inpatient and outpatient. The best choice depends on the severity of the addiction, individual needs, and the level of support required for recovery.
Behavioral Therapy for Amphetamine Addiction
- Inpatient Treatment involves living at a treatment facility 24/7. This type of treatment is most suitable for individuals with severe addiction or those who have struggled with multiple relapses. Inpatient programs provide a controlled, supportive environment where individuals can focus entirely on their recovery without external distractions. They receive constant medical supervision, including management of withdrawal symptoms and emotional support.
- Outpatient Treatment allows individuals to live at home while attending scheduled therapy and counseling sessions at a treatment facility. This option is ideal for individuals with less severe addiction or those who have completed an inpatient program and are transitioning into the next phase of recovery. Outpatient treatment offers greater flexibility so patients can continue their daily responsibilities while receiving treatment. However, it requires a strong support system and personal motivation, as the individual is not in a controlled environment throughout the day.
Behavioral therapies are a cornerstone of amphetamine addiction treatment, helping individuals identify the root causes of their addiction, modify unhealthy behaviors, and develop new coping strategies for long-term recovery. These therapies, such as cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and contingency management, focus on teaching coping strategies, problem-solving skills, and ways to handle triggers and cravings. CBT helps patients recognize and change negative thought patterns, while contingency management uses rewards to reinforce positive behaviors like abstinence. Other approaches, like motivational interviewing, aim to increase the individual’s motivation to change and engage in treatment. These evidence-based therapies not only address the physical aspects of addiction but also target the underlying psychological factors to support long-term recovery.
Medication-Assisted Treatment (MAT)
While there is currently no FDA-approved medication specifically for amphetamine addiction, medication-assisted treatment (MAT) can still play an important role in recovery. MAT combines medications with therapy to help manage withdrawal symptoms, reduce cravings, and support long-term sobriety.
For amphetamine addiction, medications may include:
- Antidepressants: These are used to address the mood disorders that often accompany amphetamine withdrawal, such as depression and anxiety. Medications like selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) or serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) can help stabilize mood and improve emotional regulation.
- Anti-anxiety medications: These can be used to alleviate symptoms of anxiety or panic that can arise during the early stages of recovery, helping individuals feel more comfortable as they work through the detox and therapy process.
- Stimulant medications: Although stimulants may seem counterintuitive, certain medications (like modafinil) are sometimes used off-label to treat stimulant addiction. These medications can help regulate energy levels and cognitive function during the recovery process.
MAT is most effective when combined with behavioral therapies, as it addresses both the physical and psychological components of addiction.
Support Groups and Peer Counseling
- Narcotics Anonymous (NA): A widely used 12-step program offering a non-judgmental space for sharing recovery journeys and staying accountable.
- SMART Recovery: A non-12-step, science-based approach that focuses on self-empowerment, offering both online and in-person meetings.
- Peer Counseling: Support from trained individuals who have experienced addiction themselves, providing guidance and building trust through shared recovery journeys.
Effective treatment for amphetamine addiction requires a multi-faceted approach, combining a range of therapy options and support systems. Whether through inpatient or outpatient programs, behavioral therapy, medication-assisted treatment, or peer support groups, individuals can find the tools they need to overcome addiction and build a foundation for lasting recovery. A comprehensive treatment plan, tailored to each individual’s specific needs, is crucial for long-term success and well-being.
How to Prevent Relapse of Amphetamine Use
Relapse is a common challenge in the recovery process, but it should not be seen as a failure. Rather, it can be an important learning experience that helps individuals identify triggers and refine their coping strategies. To prevent relapse, it’s essential for individuals in recovery to:
- Identify Triggers: Recognize stress, social situations, and emotional pain as potential triggers. Develop strategies to cope, such as managing stress and avoiding high-risk environments.
- Develop Healthy Coping Mechanisms: Practice strategies like exercise, meditation, mindfulness, journaling, and engaging in hobbies to manage emotions without resorting to substances.
- Strengthen Support Networks: Build strong relationships with supportive friends, family, peers, and recovery groups for encouragement and accountability.
- Continuing Care: Stay engaged in long-term recovery with ongoing therapy, check-ins, support groups, or intensive outpatient programs (IOP).
- Focus on Personal Growth: Set goals that align with values and long-term vision for a fulfilling life, such as improving relationships or career success, to maintain motivation and sobriety.
Supporting a Loved One in Recovery
If you have a loved one in recovery from amphetamine addiction, your support can play a crucial role in their journey. However, it’s important to remember that recovery is an individual process, and while you can offer love, encouragement, and compassion, your loved one must take ownership of their healing. Here are some ways to support them effectively:
- Be Patient and Understanding: Recovery takes time, and setbacks are normal. Be patient, offer encouragement, and remind them of your belief in their ability to overcome challenges.
- Encourage Participation in Support Networks: Support them in staying connected with treatment, therapy, and support groups. Attend family therapy sessions and show interest in their recovery process.
- Set Healthy Boundaries: Establish clear expectations and avoid enabling behaviors to promote healthy interactions and protect both of you.
- Educate Yourself: Learn about addiction and recovery to better understand their experience and reduce frustration.
- Take Care of Yourself: Prioritize your well-being by joining support groups like Al-Anon, so you can maintain your emotional health and be a more effective source of support.
For family members and loved ones, being patient, understanding, and offering consistent support can make a world of difference. Together, you can help your loved one navigate the road to recovery and rebuild their life, one day at a time.
Next Steps: Seeking Amphetamine Addiction Treatment
Overcoming amphetamine addiction is a tremendous commitment, so it’s important to select a reputable treatment center. Look for a facility that is accredited, licensed, and experienced in treating stimulant use disorders. A center with a tailored approach to amphetamine detox and recovery will address both the physical and psychological aspects of addiction. Make sure the facility offers comprehensive detox programs, therapy options (e.g., CBT, MAT), and aftercare services to support long-term recovery.
If you or someone you care about is struggling with amphetamine addiction, don’t hesitate to reach out to Legacy Healing Center. We’re here to help you explore your treatment options and support you through every step of the recovery process.
Finding Help for Recovery
- Reach Out for Help: Contact our addiction treatment facility by calling directly or filling out an online inquiry form to learn more about our programs. Our intake specialists are available to provide information and help assess your specific needs.
- Initial Assessment: The initial evaluation helps determine the severity of the addiction, any co-occurring mental health issues, and the most appropriate treatment options. The assessment will provide a clearer picture of physical, emotional, and psychological needs, which can help the facility create a personalized treatment plan.
- Review Insurance and Payment Options: Before committing to treatment, it’s important to understand the cost and insurance coverage options. Legacy Healing Center accepts private insurance, Medicaid, or even self-pay options. Our team can help you navigate the insurance verification process and identify financial assistance or sliding scale options if needed.
- Begin Treatment: Once the assessment is complete and the treatment plan is finalized, individuals can begin their detox and treatment program. Depending on the severity of addiction, treatment may involve inpatient or outpatient care, therapy, and medical monitoring.
Finding the right recovery support is a crucial step in overcoming amphetamine addiction. Whether it’s seeking treatment at a specialized facility, utilizing online resources, or connecting with helplines, there is help available. If you or someone you know is struggling with amphetamine addiction, taking the first step toward treatment can lead to lasting recovery and a brighter future. Reach out today, and know that there is support available for every stage of the recovery journey.
Compassionate Amphetamine Addiction Treatment
Recovery from amphetamine addiction is not just possible—it’s a reality that many have achieved with the right support, commitment, and treatment. While the journey may seem overwhelming, countless individuals have successfully rebuilt their lives, restored relationships, and rediscovered hope. Success stories serve as powerful reminders that professional help and personal resilience can lead to profound transformation. Taking the first step toward recovery—seeking help—may feel daunting, but it is a crucial and courageous decision that opens the door to healing.
At Legacy Healing Center, we recognize the complexities of amphetamine addiction and are dedicated to providing compassionate, individualized care throughout every stage of detox and recovery. If you or a loved one is struggling, know that you are not alone. With the right resources, therapies, and a strong support system, you can overcome addiction and work toward a healthier, sober future. Reach out today and take the first step toward lasting recovery and the life you deserve.
References
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration. (2022). 2022 National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH) results. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. https://www.samhsa.gov/data/sites/default/files/reports/rpt42731/2022-nsduh-nnr.pdf
Similar Articles
GET IN TOUCH
Contact Us
If you would like to get in touch with us or simply have any questions or comments, please call us today. Our helpline and chat are 100% confidential.
Call Us
Email Us
Corporate Headquarters